Let’s Stop Calling Climate a Green Risk
![]()
January 2026
Dear Friends,
Welcome to the great era of “green hushing.” It’s a mind-bending moment in the U.S. when climate change increasingly imperils our economy and well-being, but policymakers, scientists, businesses, teachers, reporters, federal agencies, and even park rangers are not supposed to talk about it.
The Trump administration’s animus toward “all things green” – including the scientific inquiry that enables us to measure climate change and understand its scale and scope – is working to silence climate discussion and stop critical innovation that could mitigate the threat. Banks have retreated from climate-forward lending, companies no longer speak much about their decarbonization goals, clean-energy projects that promised high-paying jobs and lower energy costs are being canceled, and the U.S. is dropping out of more than 60 international organizations involved with biodiversity, conservation, and climate change. Even the Democratic party has muted its climate messaging, recognizing its longer-term focus isn’t resonating in today’s “hair on fire” political environment.
But, unfortunately, simply “canceling” climate change won’t make it go away.
Two reports issued in January underscore how climate change’s impacts on temperatures and ecosystems are threatening our economic and geopolitical security.
In the first, the United Nations declared that the world is now in “water bankruptcy,” and water systems have been so compromised we cannot reverse the damage. Water systems are being stressed both by climate change – which alters rain patterns, concentrates water pollution, and leads to more frequent and severe droughts – and excessive uptake from aquifers, lakes, rivers, and reservoirs. Concerningly, already three-quarters of humanity live in water-stressed environments, and the challenge will only get greater as temperatures continue to rise. Water stress has been linked to the current unrest in Iran and to the Syrian civil war, and military leaders around the world warn that water scarcity and stress can be weaponized and can lead to increased global instability.
The second report, issued by UK’s Joint Intelligence Committee and based on information from MI5 and MI6, recognizes impending ecosystem collapse as a direct threat to national security. Climate change is turning rainforests into savannahs, coral reefs into lifeless skeletons, boreal forests into wildfire tinder, and is permanently melting critical mountain glaciers. Britain’s security forces predict these ecosystem losses across the world will drive up food insecurity, increase migration, change global weather patterns, and increase the risks of pandemics. These same threats, of course, are true for us on this side of the Atlantic (and climate threats have been named as such in our own intelligence assessments from 2009 until last year).
These security warnings are crystal clear: large-scale disruption of our natural world directly destabilizes our human world.
So, let’s stop calling climate a green risk. Let’s recognize it for what it really is – an economic risk, a health risk, and a security risk.
And let’s start talking loudly about it.
Sincerely,
Kathleen Biggins
Founder and President
Notable Quote
“Enough critical systems around the world have crossed these [water bankruptcy] thresholds. These systems are interconnected through trade, migration, climate feedbacks, and geopolitical dependencies, so the global risk landscape is now fundamentally altered.”
– Kaveh Madani, director of the UN University’s Institute for Water, Environment, and Health
News of Concern
After years of declining emissions, U.S. carbon pollution increased 2.4% last year, in part due to increased coal usage. Experts believe federal policies set into place in 2025 to boost fossil fuels and curtail clean energy will add to emission pressure in the future.
This push to suppress clean energy is a bigger deal than many realize. It’s not just emissions that are rising – electricity demand and prices are skyrocketing, too. Clean energy can come online in a year or two, while fossil fuel plants and nuclear plants usually take five to 10 (or more) years, respectively. So it is concerning that at a time when we need more supply immediately, almost 2,000 new power projects were canceled last year, with the vast majority (93%) of them in clean-energy generation.
The Trump administration also announced it is shutting down one of the crown jewels of climate research – the National Center for Atmospheric Research. This lab is critically important for predicting, preparing for, and responding to severe weather. The administration’s dismantling of climate institutions and initiatives is so widespread across weather tracking and preparedness, investments in clean technologies, and federal agencies that many say it will take generations to repair.

As warming air and oceans cause Greenland’s ice to melt, access to shipping lanes is expanding and long-buried, important minerals are becoming accessible. But as nations battle over who will control that power and those dollars, we are concerned that the world will lose sight of just how important this island is to our climate and the health of our planet.
One reason researching climate is so critical? To keep our homes safer from more frequent climate-enhanced natural disasters. Whether it’s bigger hailstones, faster-moving fires, or more intense hurricanes, our primary investments – our homes – are increasingly at peril. We can prepare ourselves better for the future if we understand the risks. Real estate buyers can now access climate risk information on every listing. However, this new input is roiling real estate markets because it can harm a seller’s ability to sell a home if climate metrics are poor. It’s another example of the pain ahead as we reckon with the reality of climate change, and begin to price it into our systems.
Another reckoning ahead is with our growing plastic addiction. A new report projects plastic pollution is on track to grow by an astounding 58% by 2040: if global plastic pollution were a country, it would be the world’s third-largest emitter. Plastic is a double whammy of climate woes – made from petroleum and produced with petroleum. It’s already clogging our waters and harming our bodies, and similarly to climate change, policymakers are struggling to deal with the problem.
And if you’re reading this while drinking a cup of coffee, we’ve learned that our beloved joe may taste very different in the near future. As climate change damages coffee forests, Brazilian farmers are moving away from smooth arabica beans to more bitter robusta beans, which are more heat and disease resistant.
Finally, it’s when the impacts of climate change hit home that we really begin to understand the threat. This poignant story of a Christmas village in Washington State shows just how fragile we are. Besieged by fire, storms, and power outages, this small mountain town that relies on tourism is scrambling to pick up the pieces from a holiday season that wasn’t. It’s a heartbreaker.
News of Hope
While clean-energy development is hitting headwinds in the U.S., it’s soaring globally. Some important milestones achieved in 2025:
The world produced more electricity from renewable sources than from coal.
The EU produced more electricity from wind and solar than all fossil fuels combined.
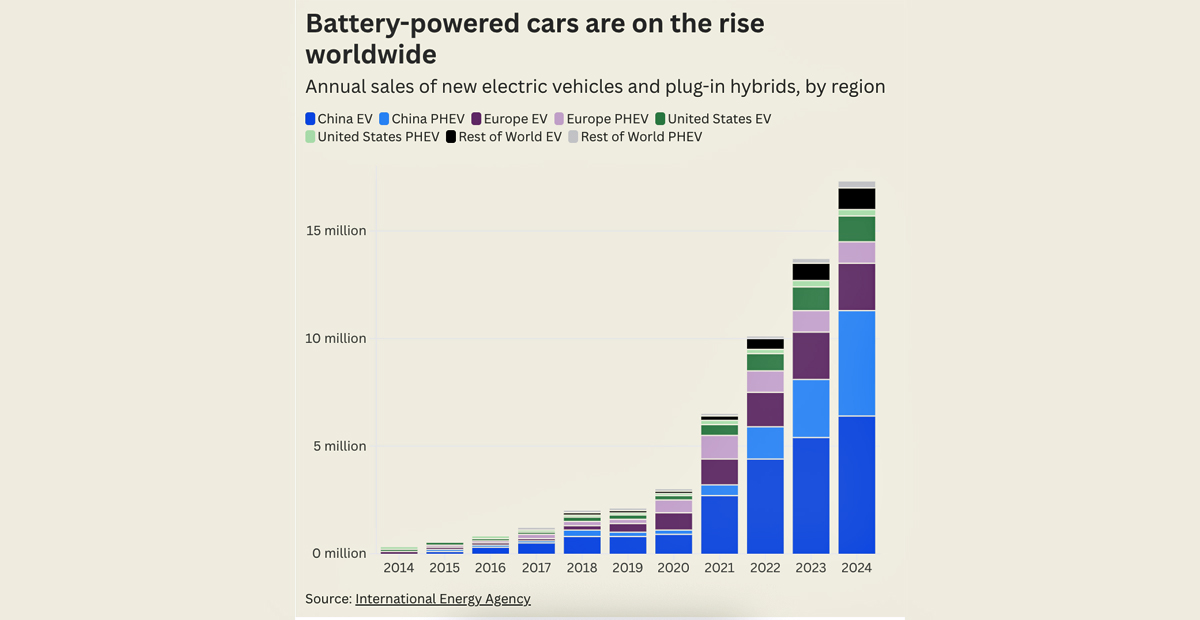
In both China and India, the world’s largest and third-largest greenhouse gas emitters respectively, coal-powered electricity generation dropped due to the rapid growth of renewables.More than 25% of all new cars purchased were electric, and sales are rising rapidly because they are now cheaper than combustion engine cars in emerging markets.
The global renewables boom is pushing investment in the cleantech sector to new heights. And it’s happening in places you might not expect. Saudi Arabia is deploying solar energy at the fastest rate in the world, on pace to generate 50% of its electricity with clean power within five years.
In the U.S., batteries are growing at astounding rates. This is a game-changer. During sunny and windy periods, we often produce an excess of cheap, clean energy and have to throw it away. With batteries, we can save that extra energy and use it at peak times after the sun has set, displacing more expensive and emission-intensive fossil fuels.
The renewables and batteries we’ve added are also making our grids more reliable – including helping us meet climate-enhanced winter storm challenges. Experts especially noted that Texas’s grid – with its expanded use of batteries and weatherization of fossil resources – bore the strain of the monster January storm that swept the country, in contrast to a 2021 storm when that grid was more heavily dependent on fossil fuels resources.
The Mid-Atlantic and Northeast corridors received good news this month on resiliency as well. Judges allowed offshore wind development to get back on track at several projects that had been stopped mid-stream last year. Offshore wind peaks in winter, which should help strengthen the grid in future winter storms, and it also can lower our costs during cold weather when our higher-priced natural gas supply is stretched due to heating and electricity demands.
In North Carolina, small mountain towns that were battered by hurricanes in 2024 are not just adapting their infrastructure, they’re re-envisioning their resilience, building microgrids, adding batteries, and thinking of new ways to stay safe from the next storm.
And in the southernmost part of the world, glaciologists are re-envisioning our future by protecting our ability to look to the past. Glaciologists fear ice cores – one of our most important lenses into the Earth’s history – will melt away. So they are building an ice storage vault in Antarctica to enable future scientists to study the ice. It’s an important reminder of how quickly nature is changing around us, and of our need to protect critical resources.
Notable Graph
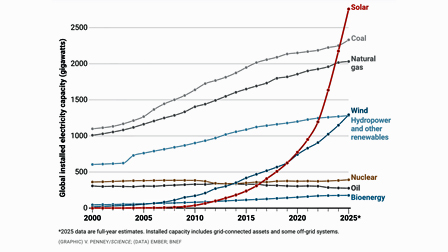
Science magazine named the renewable energy surge as its “2025 Breakthrough of the Year.” This chart shows the astounding growth of installed capacity that has been driven by falling prices of solar and other renewable sources.
Notable Video
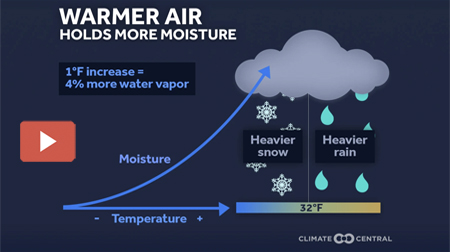
Ice, snow, polar vortex – they’re all connected to climate change, and they merged Jan. 23-25 to sweep the country in a major winter storm. This Climate Central video provides a terrific explanation of how warming global temperatures impact cold weather events.
![]()
C-Change Conversations helps people understand the science and risks of climate change and why it matters in daily life.
We frame climate change as a human and community issue – not a political one – and discuss its impacts on our jobs and economy, our health and safety, and our geopolitical stability, as well as the solutions that offer us a safer future.
C-Change seeks to bring everyone to the table for shared understanding about climate change. You can be a part of the conversation by sharing this newsletter with family, friends, and colleagues and by inviting us to talk to your community.